Implementation of Customizable Instant Search on Susper using Local Storage
Results on Susper could be instantly displayed as user types in a query. This was a strict feature till some time before, where the user doesn’t have customizable option to choose. But now one could turn off and on this feature.
To turn on and off this feature visit ‘Search Settings’ on Susper. This will be the link to it: http://susper.com/preferences and you will find different options to choose from.

How did we implement this feature?
Searchsettings.component.html:
<div> <h4><strong>Susper Instant Predictions</strong></h4> <p>When should we show you results as you type?</p> <input name="options" [(ngModel)]="instantresults" disabled value="#" type="radio" id="op1"><label for="op1">Only when my computer is fast enough</label><br> <input name="options" [(ngModel)]="instantresults" [value]="true" type="radio" id="op2"><label for="op2">Always show instant results</label><br> <input name="options" [(ngModel)]="instantresults" [value]="false" type="radio" id="op3"><label for="op3">Never show instant results</label><br> </div>
User is displayed with options to choose from regarding instant search.when the user selects a new option, his selection is stored in the instantresults variable in search settings component using ngModel.
Searchsettings.component.ts:
Later when user clicks on save button the instantresults object is stored into localStorage of the browser
onSave() { if (this.instantresults) { localStorage.setItem('instantsearch', JSON.stringify({value: true})); } else { localStorage.setItem('instantsearch', JSON.stringify({ value: false })); localStorage.setItem('resultscount', JSON.stringify({ value: this.resultCount })); } this.router.navigate(['/']); }
Later this value is retrieved from the localStorage function whenever a user enters a query in search bar component and search is made according to user’s preference.
Searchbar.component.ts
Later this value is retrieved from the localStorage function whenever a user enters a query in search bar component and search is made according to user’s preference.
onquery(event: any) { this.store.dispatch(new query.QueryAction(event)); let instantsearch = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('instantsearch')); if (instantsearch && instantsearch.value) { this.store.dispatch(new queryactions.QueryServerAction({'query': event, start: this.searchdata.start, rows: this.searchdata.rows})); this.displayStatus = 'showbox'; this.hidebox(event); } else { if (event.which === 13) { this.store.dispatch(new queryactions.QueryServerAction({'query': event, start: this.searchdata.start, rows: this.searchdata.rows})); this.displayStatus = 'showbox'; this.hidebox(event); } } }
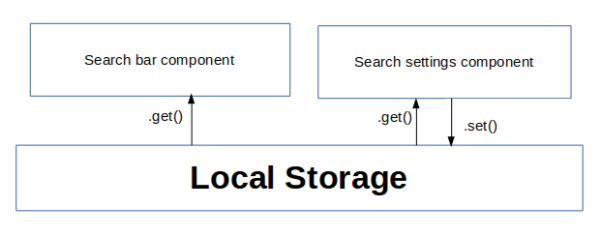
Interaction of different components here:
- First we set the instantresults object in Local Storage from search settings component.
- Later this value is retrieved and used by search bar component using localstorage.get() method to decide whether to display results instantly or not.
Below, Gif shows how you could use this feature in Susper to customise the instant results in your browser.

References:
- LocalStorage API: https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/API/Window/localStorage


























 Since this could be a very common problem on a lot of websites, this blog deals with a simple hack for it.
Since this could be a very common problem on a lot of websites, this blog deals with a simple hack for it. 
You must be logged in to post a comment.