Automatic Signing and Publishing of Android Apps from Travis
As I discussed about preparing the apps in Play Store for automatic deployment and Google App Signing in previous blogs, in this blog, I’ll talk about how to use Travis Ci to automatically sign and publish the apps using fastlane, as well as how to upload sensitive information like signing keys and publishing JSON to the Open Source repository. This method will be used to publish the following Android Apps:
Current Project Structure
The example project I have used to set up the process has the following structure:
It’s a normal Android Project with some .travis.yml and some additional bash scripts in scripts folder. The update-apk.sh file is standard app build and repo push file found in FOSSASIA projects. The process used to develop it is documented in previous blogs. First, we’ll see how to upload our keys to the repo after encrypting them.
Encrypting keys using Travis
Travis provides a very nice documentation on encrypting files containing sensitive information, but a crucial information is buried below the page. As you’d normally want to upload two things to the repo – the app signing key, and API JSON file for release manager API of Google Play for Fastlane, you can’t do it separately by using standard file encryption command for travis as it will override the previous encrypted file’s secret. In order to do so, you need to create a tarball of all the files that need to be encrypted and encrypt that tar instead. Along with this, before you need to use the file, you’ll have to decrypt in in the travis build and also uncompress it for use.
So, first install Travis CLI tool and login using travis login (You should have right access to the repo and Travis CI in order to encrypt the files for it)
Then add the signing key and fastlane json in the scripts folder. Let’s assume the names of the files are key.jks and fastlane.json
Then, go to scripts folder and run this command to create a tar of these files:
tar cvf secrets.tar fastlane.json key.jks
secrets.tar will be created in the folder. Now, run this command to encrypt the file
travis encrypt-file secrets.tar
A new file secrets.tar.enc will be created in the folder. Now delete the original files and secrets tar so they do not get added to the repo by mistake. The output log will show the the command for decryption of the file to be added to the .travis.yml file.
Decrypting keys using Travis
But if we add it there, the keys will be decrypted for each commit on each branch. We want it to happen only for master branch as we only require publishing from that branch. So, we’ll create a bash script prep-key.sh for the task with following content
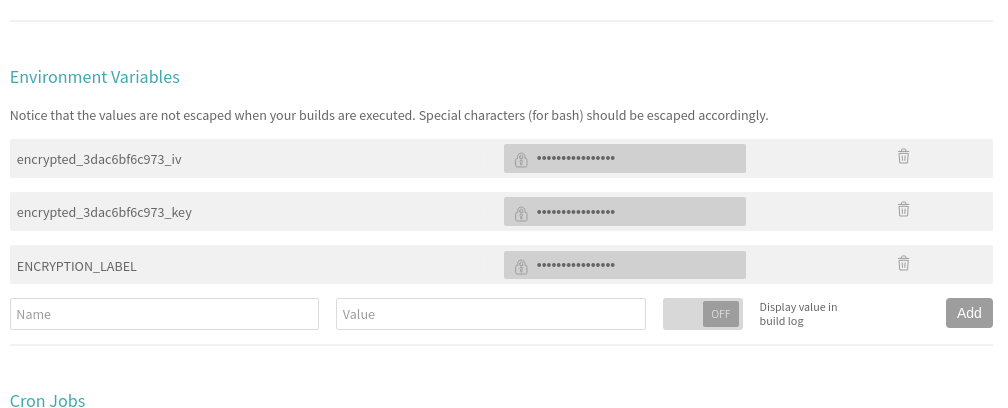
#!/bin/sh set -e export DEPLOY_BRANCH=${DEPLOY_BRANCH:-master} if [ "$TRAVIS_PULL_REQUEST" != "false" -o "$TRAVIS_REPO_SLUG" != "iamareebjamal/android-test-fastlane" -o "$TRAVIS_BRANCH" != "$DEPLOY_BRANCH" ]; then echo "We decrypt key only for pushes to the master branch and not PRs. So, skip." exit 0 fi openssl aes-256-cbc -K $encrypted_4dd7_key -iv $encrypted_4dd7_iv -in ./scripts/secrets.tar.enc -out ./scripts/secrets.tar -d tar xvf ./scripts/secrets.tar -C scripts/
Of course, you’ll have to change the commands and arguments according to your need and repo. Specially, the decryption command keys ID
The script checks if the repo and branch are correct, and the commit is not of a PR, then decrypts the file and extracts them in appropriate directory
Before signing the app, you’ll need to store the keystore password, alias and key password in Travis Environment Variables. Once you have done that, you can proceed to signing the app. I’ll assume the variable names to be $STORE_PASS, $ALIAS and $KEY_PASS respectively
Signing App
Now, come to the part in upload-apk.sh script where you have the unsigned release app built. Let’s assume its name is app-release-unsigned.apk.Then run this command to sign it
cp app-release-unsigned.apk app-release-unaligned.apk jarsigner -verbose -tsa http://timestamp.comodoca.com/rfc3161 -sigalg SHA1withRSA -digestalg SHA1 -keystore ../scripts/key.jks -storepass $STORE_PASS -keypass $KEY_PASS app-release-unaligned.apk $ALIAS
Then run this command to zipalign the app
${ANDROID_HOME}/build-tools/25.0.2/zipalign -v -p 4 app-release-unaligned.apk app-release.apk
Remember that the build tools version should be the same as the one specified in .travis.yml
This will create an apk named app-release.apk
Publishing App
This is the easiest step. First install fastlane using this command
gem install fastlane
Then run this command to publish the app to alpha channel on Play Store
fastlane supply --apk app-release.apk --track alpha --json_key ../scripts/fastlane.json --package_name com.iamareebjamal.fastlane
You can always configure the arguments according to your need. Also notice that you have to provide the package name for Fastlane to know which app to update. This can also be stored as an environment variable.
This is all for this blog, you can read more about travis CLI, fastlane features and signing process in these links below:
- Travis CLI
https://github.com/travis-ci/travis.rb#readme - Fastlane Supply
https://github.com/fastlane/fastlane/tree/master/supply - Android App Signing
https://developer.android.com/studio/publish/app-signing.html