SUSI Web Chat now replies to voice inputs. To achieve this, I made use of the Web Speech API. The voice input saves one from the pain of typing and it’s a much needed feature for the Web Chat and to maintain the similarity with the other SUSI Android and SUSI iOS clients.
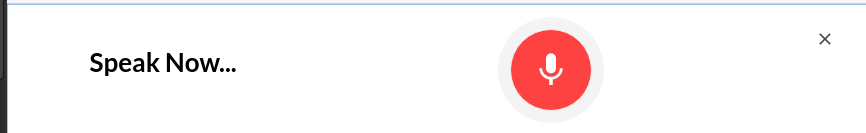
To test the feature out in SUSI Web Chat, click on the microphone icon beside the text area on chat.susi.ai.

Say the message once the dialog appears, and you will see the message being sent to the Chat List rendered in text.
Let’s achieve the same result following the steps below.
- First, initialize the class Voice Recognition with defaults for the Speech Recognition, for that we create a file VoiceRecognition.js
- We first initialize the Speech Recognition API with the window object.
- We warn the User with a console message if there is no Speech Recognition API available.
- If it’s available call the recognition function using the following line
this.recognition = this.createRecognition(SpeechRecognition)
// Initialise the Speech recognition API
const SpeechRecognition = window.SpeechRecognition
|| window.webkitSpeechRecognition
|| window.mozSpeechRecognition
|| window.msSpeechRecognition
|| window.oSpeechRecognition
// Warn the user if not available otherwise call the createRecognition function
if (SpeechRecognition != null) {
this.recognition = this.createRecognition(SpeechRecognition)
} else {
console.warn('The current browser does not support the SpeechRecognition API.');
}
}
- Then we write the createRecognition function
- We set our defaults first as “continuous – true, interimResults – false, and language – ‘en-US’ ”
- We pass these options to the recognition object that we created in the above step and finally return the recognition object.
createRecognition = (SpeechRecognition) => {
const defaults = {
continuous: true,
interimResults: false,
lang: 'en-US'
}
const options = Object.assign({}, defaults, this.props)
let recognition = new SpeechRecognition()
recognition.continuous = options.continuous
recognition.interimResults = options.interimResults
recognition.lang = options.lang
return recognition
}
- Initialize all the helper functions to be passed as props.
- start – This method starts the recognition and invokes the Mic of the browser. It also checks if the browser has the access to the user’s Mic.
- stop – Stop method closes the Mic and returns the audio captured so far.
- abort – Abort method stops the SpeechRecognition service.
- onspeechend – This method is called if there is any inactivity and there is no voice input. Hence, stops the recognition service.
- componentWillReceiveProps – This method waits for the stop method and calls it when it has received the stop object.
- componentWIllUnmount – This method is invoked just before the component is about to unmount and therefore its function is to abort the Speech Recognition Service
- render – We return null as there is nothing to return in this component and all the converted text of the captured Speech will be sent to the parent element.
start = () => {
this.recognition.start()
}
stop = () => {
this.recognition.stop()
}
abort = () => {
this.recognition.abort()
}
onspeechend = () => {
console.log('no sound detected');
this.recognition.stop()
}
componentWillReceiveProps ({ stop }) {
if (stop) {
this.stop()
}
}
componentWillUnmount () {
this.abort()
}
render () {
return null
}
- Add event listeners to start and stop functions inside componentDidMount() to ensure every action that we want to perform from the parent element is after the component has successfully mounted itself.
- start – The start method is set with an action start so that we can pass the required action name to the VoiceRecognition component that we created
- end – The end method similarly is set with an action end
- After setting up the actions we finally call the bindResult function with the result that we received.
componentDidMount () {
const events = [
{ name: 'start', action: this.props.onStart },
{ name: 'end', action: this.props.onEnd },
{ name: 'onspeechend', action: this.props.onspeechend }
]
events.forEach(event => {
this.recognition.addEventListener(event.name, event.action)
})
this.recognition.addEventListener('result', this.bindResult)
this.start()
}
- Bind the result and send it as the props to the parent element.
- Combine all interim results of the recognition and send it to the onResult function as finalTranscript
- The function bindResult – The function bindResult does all the binding of the interim results that we received and output a final result as finalTranscript.
- Lastly, we add the prop validations to ensure the correct props are being passed to our VoiceRecognition component.
// bindResult function
bindResult = (event) => {
let interimTranscript = ''
let finalTranscript = ''
// Bind all the results to finalTranscript
for (let i = event.resultIndex; i < event.results.length; ++i) {
if (event.results[i].isFinal) {
finalTranscript += event.results[i][0].transcript
} else {
interimTranscript += event.results[i][0].transcript
}
}
this.props.onResult({ interimTranscript, finalTranscript })
}
// Add Prop Validations
VoiceRecognition.propTypes = {
onStart: PropTypes.func,
onEnd : PropTypes.func,
onResult: PropTypes.func,
Onspeechend: PropTypes.func,
continuous: PropTypes.bool,
lang: PropTypes.string,
stop: PropTypes.bool
};
// Finally export the VoiceRecognition Component
export default VoiceRecognition
- Lastly, call the VoiceRecogntion component and pass the props from the MessageComposer Section to it in the following way.
- Initialize the default state in the constructor inside this.state
this.state = {
text: '',
start: false, // Starting the VoiceRecognition
stop: false, // Stop the VoiceRecognition
open: false, // Maintain the modal state
result:'' // Maintain the result state
};
- onStart function to call the VoiceRecognition component only when the Mic Button is pressed.
- onEnd to end the Speech Recognition service.
- onResult to send the message through the Actions.createMessage() function
onResult = ({interimTranscript,finalTranscript }) => {
let result = interimTranscript;
let voiceResponse = false;
this.setState({result:result});
if(finalTranscript) {
result = finalTranscript;
this.setState({
start: false,
result:result,
stop: false,
open:false,
animate:false
});
if(this.props.speechOutputAlways || this.props.speechOutput){
voiceResponse = true;
}
Actions.createMessage(result, this.props.threadID, voiceResponse);
setTimeout(()=>this.setState({result: ''}),400);
this.Button = <Mic />
}
}
- Fire the component based on the value of start variable and pass the requisite props as given below in the code.
// Only when the start is ‘true’ call the VoiceRecognition component
{this.state.start && (
<VoiceRecognition
onStart={this.onStart}
onEnd={this.onEnd}
onResult={this.onResult}
continuous={true}
lang="en-US"
stop={this.state.stop}
/>
)}
- Update the text in the “Speak Now” Dialog to show the user the Speech to Text conversion
- Update the text in the Modal when it is converted from Speech to Text, i.e. when we set the state of the result variable.
{this.state.result !=='' ? this.state.result :
'Speak Now...'}
To get access to the full code, go to the repository https://github.com/fossasia/chat.susi.ai
Resources









You must be logged in to post a comment.